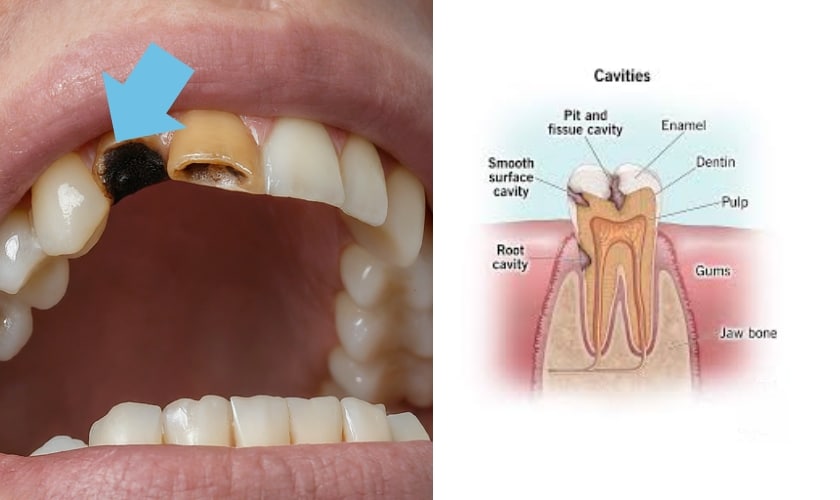
How To Avoid Cavity Pain
Cavities. Just the word itself can send shivers down your spine. That sharp, throbbing pain that seems to come out of nowhere is enough to make anyone reach for the pain relievers. But what if you could avoid that agony altogether?
This guide dives deep into the world of cavities, exploring not just the symptoms and causes, but also the most crucial aspect: How To Avoid Cavity Pain. We’ll explore prevention tips, home remedies for temporary relief, and professional treatment options to keep your smile healthy and pain-free.
What is a Cavity?
A cavity, also known as dental caries, is a hole that forms in your tooth due to plaque buildup. Plaque is a sticky film that harbors bacteria. These bacteria feed on sugars and starches in your food, producing acid as a byproduct. This acid erodes the enamel (the hard outer layer) of your tooth, eventually creating a cavity.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), nearly 20% of adults aged 20 to 44 have at least one untreated cavity in a permanent tooth. Ouch! That’s a lot of potential pain.
Let’s delve into the telltale signs of a cavity so you can identify it early on.
Symptoms of a Cavity
Early cavities might not cause any pain at all. However, as the cavity grows, you might experience some of the following symptoms:
1. Toothache:
This is the most common symptom, ranging from a mild ache to a sharp, throbbing pain.
2. Sensitivity to hot or cold:
Teeth with cavities may become sensitive to extreme temperatures.
3. Pain when biting:
Chewing can cause discomfort if the cavity affects a deeper layer of the tooth.
4. Visible holes or pits in the tooth:
You might be able to see a dark spot or a hole in the tooth’s surface.
5. Stains on the tooth:
The tooth may appear brown, yellow, or black.
6. Bad breath (halitosis):
Cavities can trap food particles, leading to bad breath.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a dentist as soon as possible. Early detection and treatment can prevent the cavity from worsening and causing more extensive damage.
Causes of Cavities
Now that we know the symptoms, let’s understand what triggers this unwanted guest in your mouth. Here are the main culprits behind cavities:
1. Sugary and starchy foods and drinks:
Bacteria in your mouth thrive on sugar and starches. These foods create an acidic environment that weakens tooth enamel.
2. Poor oral hygiene:
Brushing your teeth twice a day and flossing once a day removes plaque and food particles that contribute to cavities.
3. Dry mouth:
Saliva helps wash away food particles and neutralize acids in your mouth. Certain medications and medical conditions can cause dry mouth, increasing the risk of cavities.
4. Frequent snacking:
Constantly snacking throughout the day allows bacteria more opportunities to produce acid and attack your teeth.
5. Chewing on hard objects:
This can chip or crack your teeth, creating entry points for bacteria and cavities.
By understanding these causes, you can take steps to prevent cavities and avoid the pain they bring.
How to Stop a Cavity from Hurting?
Experiencing cavity pain can be very uncomfortable, but there are ways to alleviate it until you can see a dentist. Here are some effective strategies:
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relief: Medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Topical Treatments: Applying clove oil or a numbing dental gel directly to the affected area can provide temporary relief.
- Saltwater Rinse: Rinsing your mouth with warm salt water can help reduce swelling and disinfect the area.
- Cold Compress: Applying a cold compress to the outside of your cheek can help numb the pain and reduce swelling.
- Avoid Trigger Foods: Steer clear of hot, cold, or sugary foods and drinks that can exacerbate the pain.
These methods can offer temporary relief but should not replace professional dental care.
Can You Heal a Cavity Naturally?
While there is no scientific evidence that cavities can be completely healed naturally, certain measures can help remineralize tooth enamel and slow the progression of decay. These include:
- Fluoride Treatments: Fluoride helps remineralize enamel and can be found in toothpaste, mouth rinses, and professional treatments.
- Calcium and Phosphate: Consuming foods rich in these minerals can support enamel health.
- Xylitol: A natural sweetener that can reduce the growth of cavity-causing bacteria.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water, especially fluoridated water, can help wash away food particles and acids.
These methods can support oral health but are not substitutes for professional dental treatment.
Can You Stop a Cavity Once It Starts?
Once a cavity has formed, it cannot be reversed, but its progression can be halted with proper care. Here are some steps to manage a cavity once it starts:
- Good Oral Hygiene: Brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and flossing can prevent further decay.
- Dental Sealants: These protective coatings applied to the chewing surfaces of back teeth can prevent cavities.
- Regular Dental Visits: Professional cleanings and check-ups can catch cavities early and treat them before they worsen.
- Healthy Diet: Reducing sugar intake and eating a balanced diet can help maintain strong teeth.
These practices can help manage cavities and prevent them from getting worse.
Can I Stop a Cavity from Getting Worse?
Stopping a cavity from getting worse requires consistent and effective oral care. Consider the following tips:
- Fluoride Use: Use fluoride toothpaste and consider professional fluoride treatments.
- Regular Brushing and Flossing: Maintain a rigorous oral hygiene routine.
- Dietary Changes: Limit sugary and acidic foods and drinks.
- Chewing Sugar-Free Gum: This can help increase saliva production, which protects against decay.
- Dental Visits: Regular check-ups can ensure any developing issues are addressed promptly.
Proactive dental care is key to preventing cavities from worsening.
Will a Cavity Eventually Stop Hurting?
Cavity pain may temporarily subside, but this does not mean the problem has resolved. Ignoring cavity pain can lead to more severe issues, including:
- Infection: Untreated cavities can lead to tooth infections, requiring more extensive treatment like root canals.
- Tooth Loss: Severe decay can result in the loss of the affected tooth.
- Spread of Infection: Dental infections can spread to other parts of the body, causing serious health complications.
It is essential to seek dental treatment even if the pain subsides temporarily.
At What Stage Does a Cavity Hurt?
Cavities progress through several stages, with pain typically occurring in the later stages:
- Early Stage: Small white spots or discoloration on the enamel, usually painless.
- Enamel Decay: Slight sensitivity as the decay penetrates the enamel.
- Dentin Decay: Increased sensitivity and pain, especially when consuming hot, cold, or sweet foods and drinks.
- Pulp Involvement: Severe pain and potential infection as decay reaches the tooth’s pulp.
- Abscess Formation: Intense pain, swelling, and possible fever as an abscess forms at the root of the tooth.
Pain usually begins when the decay reaches the dentin and worsens as it progresses.
Treatment Options
When it comes to treating cavities, several options are available depending on the severity of the decay:
- Fluoride Treatments: For early-stage cavities, fluoride treatments can help restore enamel.
- Fillings: Composite resins or amalgam fillings are used to fill cavities after decay removal.
- Crowns: For extensive decay, a crown may be placed over the tooth.
- Root Canals: When decay reaches the tooth pulp, a root canal is necessary to remove infected tissue.
- Tooth Extraction: In severe cases, the tooth may need to be removed.
Consulting with a dentist will determine the best treatment option for your specific situation.
When to See a Dentist
If you are in Riverside It’s crucial to see a best dentist in Riverside, Califonia if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Persistent Toothache: Ongoing pain that doesn’t go away.
- Sensitivity: Pain or discomfort when eating or drinking.
- Visible Cavities: Noticeable holes or pits in your teeth.
- Gum Swelling: Swollen or bleeding gums.
- Bad Breath: Chronic bad breath that doesn’t improve with brushing and flossing.
Regular dental visits are essential for maintaining oral health and catching cavities early.
Conclusion
Cavity pain is not just a minor inconvenience; it can significantly impact your quality of life. Understanding how to avoid cavity pain through effective prevention and treatment strategies is key to maintaining good oral health. By recognizing the symptoms early, addressing the causes, and seeking appropriate treatment, you can keep your teeth healthy and pain-free. Remember, regular dental visits and good oral hygiene practices are your best defenses against cavities.
Resources
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): https://www.cdc.gov/oral-health/index.html offers a wealth of information on oral health, including cavity prevention and treatment.
American Dental Association (ADA): https://www.ada.org/ provides patient resources on various dental topics, including cavities and how to find a dentist.
National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR): https://www.nidcr.nih.gov/ is a part of the National Institutes of Health and offers research-based information on dental conditions.